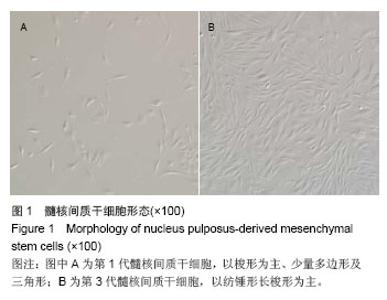
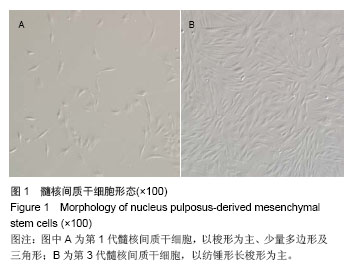
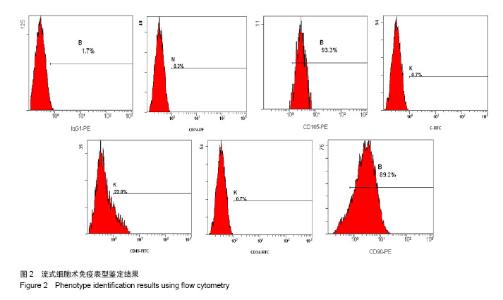
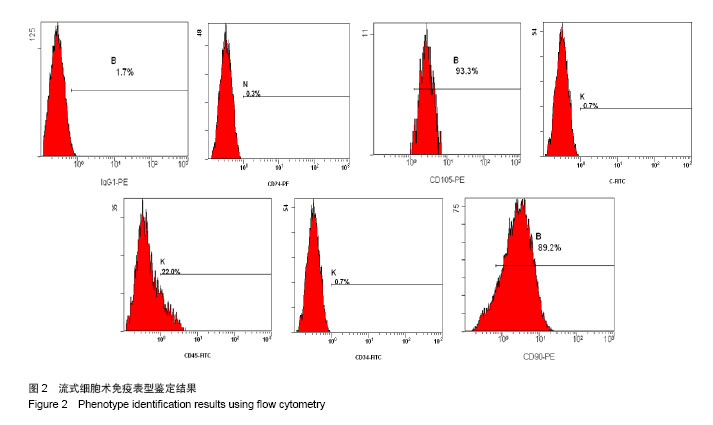
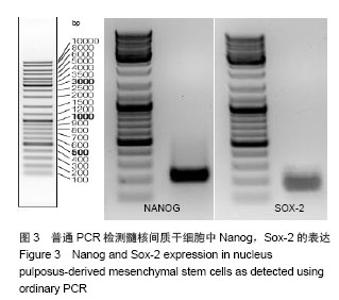
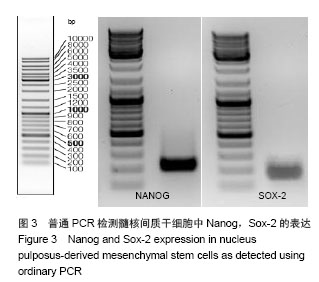
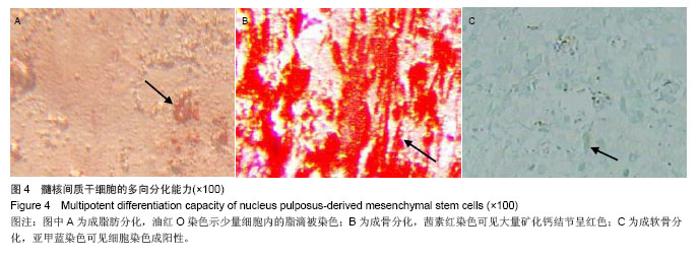
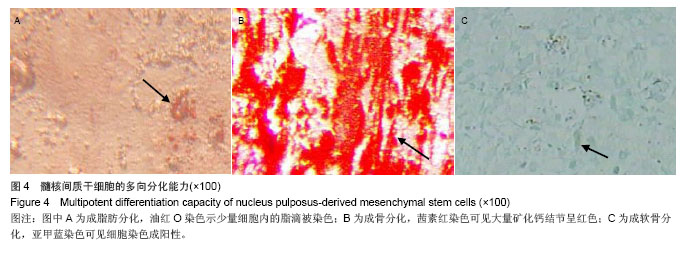
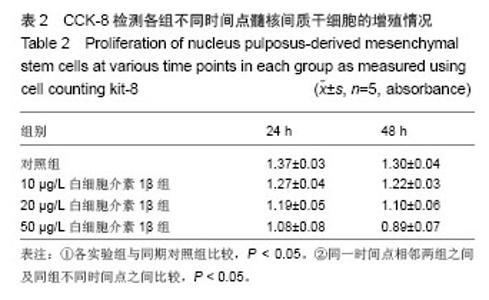
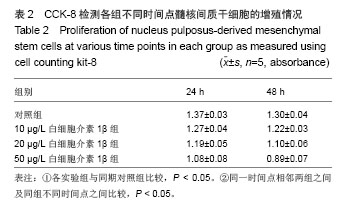
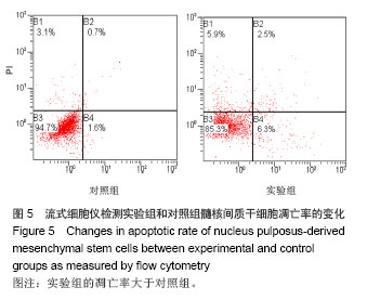
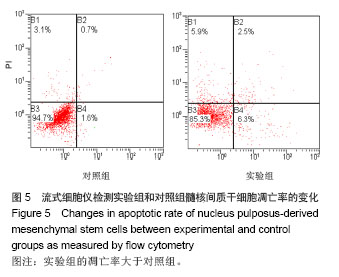
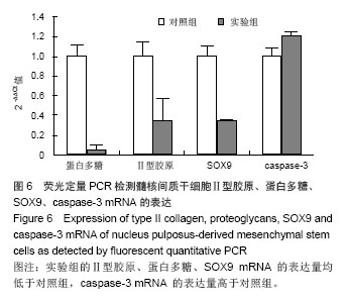
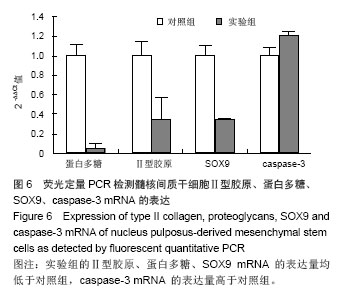
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (28): 4437-4443.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.28.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Interleukin-1 beta affects the biological properties of rat nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells
Zhang Ning1, Guan Xiao-ming1, Ma Xun2, Zhang Li2, Zhang Hui1, Song Liang1
- 1 Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 2 Department of Orthopedics, Shanxi Dayi Hospital, Taiyuan 030032, Shanxi Province, China
-
Online:2014-07-02Published:2014-07-02 -
Contact:Ma Xun, Master, Professor, Department of Orthopedics, Shanxi Dayi Hospital, Taiyuan 030032, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Zhang Ning, Master, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province, No. 2011011042-3; the Undergraduate Innovation and Entrepreneurship Project of Taiyuan City, No. 120164064; the Excellent Innovation Project of Shanxi Province for Postgraduates, No. 20113069
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Ning, Guan Xiao-ming, Ma Xun, Zhang Li, Zhang Hui, Song Liang. Interleukin-1 beta affects the biological properties of rat nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(28): 4437-4443.
share this article
| [1]Nachemson A. Is there such a thing as degenerative disc disease? In: Gunzburg R, Szpalski M, Andersson GB, ed. Degenerative disc disease. Philadelphia, Lippincott Williams Wilkins, 2004: 1-5. [2]Kara B, Tulum Z, Acar U. Functional results and the risk factors of reoperations after lumbar disc surgery. Eur Spine J. 2005;14(1):43-48. [3]Miller JA, Schmatz C, Schultz AB. Lumbar disc degeneration: correlation with age, sex, and spine level in 600 autopsy specimens. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1988;13(2):173-178. [4]Buckwalter JA.Aging and degeneration of the human intervertebral disc.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995;20(11): 1307-1314. [5]Boos N, Weissbach S, Rohrbach H,et al.Classification of age-related changes in lumbar intervertebral discs: 2002 Volvo Award in basic science.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27(23):2631-2644. [6]Kuslich SD, Ulstrom CL, Michael CJ.The tissue origin of low back pain and sciatica: a report of pain response to tissue stimulation during operations on the lumbar spine using local anesthesia.Orthop Clin North Am. 1991;22(2):181-187. [7]Schwarzer AC, Aprill CN, Derby R,et al.The relative contributions of the disc and zygapophyseal joint in chronic low back pain.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994;19(7):801-806. [8]Leung VY, Chan D, Cheung KM.Regeneration of intervertebral disc by mesenchymal stem cells: potentials, limitations, and future direction.Eur Spine J. 2006;15 Suppl 3:S406-413. [9]Katz JN.Lumbar disc disorders and low-back pain: socioeconomic factors and consequences.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88 Suppl 2:21-24. [10]Freeman BJ, Davenport J.Total disc replacement in the lumbar spine: a systematic review of the literature.Eur Spine J. 2006;15 Suppl 3:S439-447. [11]van den Eerenbeemt KD, Ostelo RW, van Royen BJ,et al.Total disc replacement surgery for symptomatic degenerative lumbar disc disease: a systematic review of the literature.Eur Spine J. 2010;19(8):1262-1280. [12]Etebar S, Cahill DW. Risk factors for adjacent-segment failure following lumbar fixation with rigid instrumentation for degenerative instability.J Neurosurg. 1999;90(2 Suppl): 163-169. [13]Sakai D.Stem cell regeneration of the intervertebral disk. Orthop Clin North Am. 2011;42(4):555-562. [14]Richardson SM, Hoyland JA, Mobasheri R,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells in regenerative medicine: opportunities and challenges for articular cartilage and intervertebral disc tissue engineering.J Cell Physiol. 2010;222(1):23-32. [15]Hoogendoorn RJ, Lu ZF, Kroeze RJ,et al.Adipose stem cells for intervertebral disc regeneration: current status and concepts for the future.J Cell Mol Med. 2008;12(6A):2205-2216. [16]He F, Pei M.Rejuvenation of nucleus pulposus cells using extracellular matrix deposited by synovium-derived stem cells.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(6):459-469. [17]Orozco L, Soler R, Morera C, et al.Intervertebral disc repair by autologous mesenchymal bone marrow cells: a pilot study. Transplantation. 2011;92(7):822-828. [18]Chan SC, Gantenbein-Ritter B, Leung VY,et al.Cryopreserved intervertebral disc with injected bone marrow-derived stromal cells: a feasibility study using organ culture.Spine J. 2010; 10(6):486-496. [19]Serigano K, Sakai D, Hiyama A,et al.Effect of cell number on mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in a canine disc degeneration model.J Orthop Res. 2010;28(10):1267-1275. [20]Risbud MV, Guttapalli A, Tsai TT,et al.Evidence for skeletal progenitor cells in the degenerate human intervertebral disc.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(23):2537-2544. [21]Blanco JF, Graciani IF, Sanchez-Guijo FM,et al.Isolation and characterization of mesenchymal stromal cells from human degenerated nucleus pulposus: comparison with bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells from the same subjects.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(26):2259-2265. [22]Erwin WM, Islam D, Eftekarpour E,et al.Intervertebral disc-derived stem cells: implications for regenerative medicine and neural repair.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38(3):211-216. [23]张丽. hTERT基因修饰的椎间盘髓核细胞永生化研究及干细胞样髓核细胞的分离鉴定[D]. 太原:山西医科大学,2011. [24]关晓明,马迅,张丽,等. 不同来源椎间盘髓核间质干细胞特性及其多向分化能力研究[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2012,32(7):686-692. [25]Buckwalter JA.Aging and degeneration of the human intervertebral disc.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995;20(11): 1307-1314. [26]Wuertz K, Godburn K, Neidlinger-Wilke C,et al.Behavior of mesenchymal stem cells in the chemical microenvironment of the intervertebral disc.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(17): 1843-1849. [27]Peng B, Hao J, Hou S,et al. Possible pathogenesis of painful intervertebral disc degeneration.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31(5):560-566. [28]Freemont AJ.The cellular pathobiology of the degenerate intervertebral disc and discogenic back pain.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009;48(1):5-10. [29]Richardson SM, Mobasheri A, Freemont AJ,et al. Intervertebral disc biology, degeneration and novel tissue engineering and regenerative medicine therapies.Histol Histopathol. 2007;22(9):1033-1041. [30]Yoshida M, Nakamura T, Sei A,et al. Intervertebral disc cells produce tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-1beta, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 immediately after herniation: an experimental study using a new hernia model.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(1):55-61. [31]Fujita K, Nakagawa T, Hirabayashi K,et al.Neutral proteinases in human intervertebral disc. Role in degeneration and probable origin.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18(13): 1766-1773. [32]Kang JD, Georgescu HI, McIntyre-Larkin L,et al. Herniated cervical intervertebral discs spontaneously produce matrix metalloproteinases, nitric oxide, interleukin-6, and prostaglandin E2.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995;20(22): 2373-2378. [33]Liu J, Roughley PJ, Mort JS.Identification of human intervertebral disc stromelysin and its involvement in matrix degradation.J Orthop Res. 1991;9(4):568-575. [34]Takahashi H, Suguro T, Okazima Y,et al.Inflammatory cytokines in the herniated disc of the lumbar spine.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21(2):218-224. [35]Podichetty VK.The aging spine: the role of inflammatory mediators in intervertebral disc degeneration.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2007;53(5):4-18. [36]Guilak F, Cohen DM, Estes BT,et al.Control of stem cell fate by physical interactions with the extracellular matrix.Cell Stem Cell. 2009;5(1):17-26. [37]彭宝淦,贾连顺. 腰椎间盘突出症炎症机理研究概述[J].中华外科杂志,1998,36(12):724. [38]Kang JD, Georgescu HI, McIntyre-Larkin L,et al.Herniated cervical intervertebral discs spontaneously produce matrix metalloproteinases, nitric oxide, interleukin-6, and prostaglandin E2.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995;20(22):2373-2378. [39]Takahashi H, Suguro T, Okazima Y,et al.Inflammatory cytokines in the herniated disc of the lumbar spine.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21(2):218-224. [40]Rand N, Reichert F, Floman Y,et al.Murine nucleus pulposus-derived cells secrete interleukins-1-beta, -6, and -10 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in cell culture.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997;22(22):2598-601. [41]Kang JD, Stefanovic-Racic M, McIntyre LA,et al.Toward a biochemical understanding of human intervertebral disc degeneration and herniation. Contributions of nitric oxide, interleukins, prostaglandin E2, and matrix metalloproteinases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997;22(10):1065-1073. [42]胡宝山,芮钢,杨茂伟,等.白细胞介素-1β对椎间盘蛋白多糖代谢的影响[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志,2008,7(1): 31-32. [43]Doita M, Kanatani T, Harada T,et al.Immunohistologic study of the ruptured intervertebral disc of the lumbar spine.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21(2):235-241. [44]Rannou F, Richette P, Benallaoua M,et al.Cyclic tensile stretch modulates proteoglycan production by intervertebral disc annulus fibrosus cells through production of nitrite oxide. J Cell Biochem. 2003;90(1):148-157. [45]Shen B, Melrose J, Ghosh P,et al.Induction of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -3 activity in ovine nucleus pulposus cells grown in three-dimensional agarose gel culture by interleukin-1beta: a potential pathway of disc degeneration. Eur Spine J. 2003;12(1):66-75. [46]Le Maitre CL, Freemont AJ, Hoyland JA.The role of interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis of human intervertebral disc degeneration.Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(4):R732-745. [47]Solovieva S, Lohiniva J, Leino-Arjas P,et al.Intervertebral disc degeneration in relation to the COL9A3 and the IL-1ss gene polymorphisms.Eur Spine J. 2006;15(5):613-619. [48]Dendorfer U, Oettgen P, Libermann TA.Interleukin-6 Gene Expression by Prostaglandins and Cyclic AMP Mediated by Multiple Regulatory Elements.Am J Ther. 1995;2(9):660-665. [49]Jimbo K, Park JS, Yokosuka K,et al.Positive feedback loop of interleukin-1beta upregulating production of inflammatory mediators in human intervertebral disc cells in vitro.J Neurosurg Spine. 2005;2(5):589-595. [50]Le Maitre CL, Hoyland JA, Freemont AJ.Catabolic cytokine expression in degenerate and herniated human intervertebral discs: IL-1beta and TNFalpha expression profile.Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(4):R77. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Li Cai, Zhao Ting, Tan Ge, Zheng Yulin, Zhang Ruonan, Wu Yan, Tang Junming. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of skeletal muscle myoblast [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1050-1055. |
| [14] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [15] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||